Triterpene glycosides, also known as saponines,
represent one of numerous class of natural compounds. They serve
as secondary metabolites of mixed biosynthesis, like alkaloids, flavonoids,
oligosaccharides etc.).
Growing interest to natural saponines caused as
by scientific aspects of extraction and structural analysis of these compound,
as by the fact of their wide spectrum of biological activities, like bacteri˝idal,
fungicidal, antvirial, cytotoxic, anticancer, ichtiotoxic, spermicidal,
cardiovsicular, analhetic, antiallergic and many others.
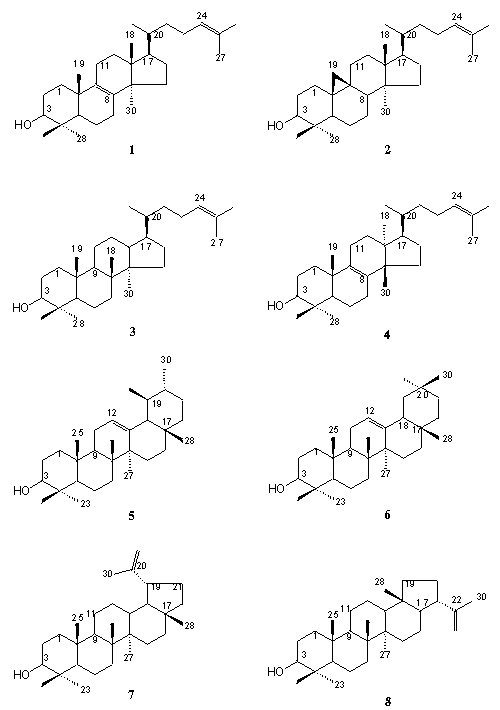
Saponines are glycosides of tpiterpenoids, which
form one of the most numerous group of natural terpenoids. The main groups
of triterpenoids and their glycosides represented by tetracyclic derivatives
of lanostane 1, cycloartane 2, dammarane 3, eufane
4,
and pentacyclic derivatives of ursane (alpha-amirine) 5 , lanostane
(beta-amirine) 6, lupane 7, and hopane
8. (Pic.1)
 |
|
|
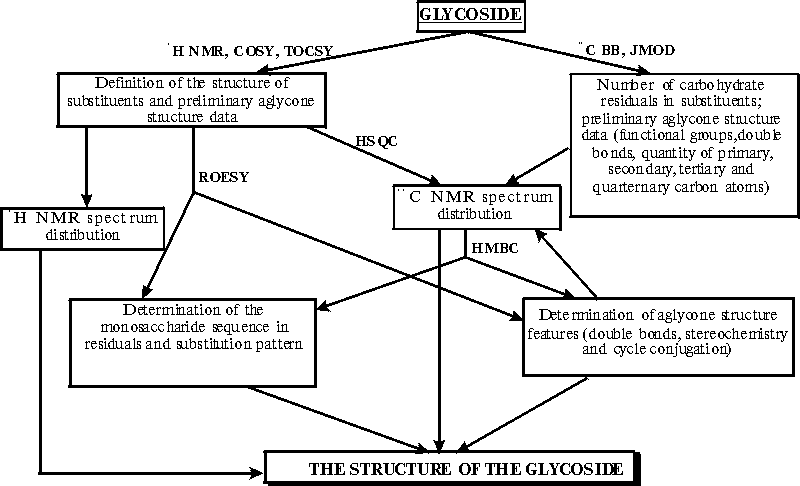
There are many methods for determination of the structure of glycosides,
such as chemical analysis, IR, UV, and NMR spectroscopy, mass-spectrometry
and X-ray structure analysis. But most suitable method is NMR as non-destructive
and informative one. We developed reserach scheme for triterpene
glycosides which allows us make complete distrubutions of peaks both in
1H
NMR and 13C NMR spectra (Pic. 2)
 |
|
|
Under construction
Updated 18.10.2000